Email Authentication in the Era of Phishing and Spam: The Role of DMARC, DKIM, and SPF
In this article, we will explore the role of three key email authentication protocols: DMARC, DKIM, and SPF, and how they play a vital role in the era of phishing and email spam protection for businesses and individuals.
Email is a crucial communication tool for businesses to interact with customers, clients, and employees. However, it has become a prime target for phishing and spam. Organizations, thus, need to understand the role of email authentication protocols such as DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and how these can be used to ensure the best protection against email-based attacks.
Let’s delve deeper into how these technologies work and how they can help safeguard your organization’s email communications.
Understanding the Threat of Phishing and Email Spam
The threat of phishing and spam to businesses is paramount in the current digital landscape. These nefarious activities represent a significant security vulnerability, as they often target unsuspecting individuals to extract sensitive information for financial gain.
Here are a few statistics to paint a clearer picture:
- Recent data reveals that in 2023, the number of emails sent and received worldwide each day has increased by 4.3%, totaling 347.3 billion.
- In 2021, a staggering 283 billion spam emails were identified out of 336.41 billion emails sent.
- Predictions indicate that by 2025, the financial damage caused by hackers is expected to exceed $10.5 trillion.

Phishing and spam can potentially cause significant financial and reputational damage to businesses, making it imperative for organizations to take proactive measures to protect themselves and their stakeholders from these threats. Let us see the role of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC in email authentication.
How SPF Lays the Foundation of Email Authentication
The SPF protocol serves as the foundation for a tripartite standard of email authentication by providing a framework for verifying the ownership of a domain, which is of paramount importance in realizing the benefits of DMARC and DKIM as SPF records enable email systems to authenticate that the domain from which an email is being sent is, in fact, a domain that has been authenticated as the owner and controller of said domain.
The SPF protocol defines the utilization of DNS (Domain Name System) records and the exchange of SPF information between email servers, all with the objective of authenticating email servers. However, it is worth noting that SPF does not specify what actions should be taken with the information it provides. And this is the point where DKIM and DMARC protocols come into play.
Email Authentication with DKIM and DMARC
Mail sent by servers that implement DKIM are digitally signed, and these digital signatures are authenticated using public keys associated with the sending server. These public keys are stored in DKIM records, which are added to the DNS records of the sending domain’s owner. The DKIM signature enables domain authentication, thus validating that the email genuinely came from the specified domain.
The DMARC protocol relies on both SPF and DKIM to authenticate email. DMARC allows domain owners to control unauthenticated messages and specify what the receiving servers should do to unauthorized or unauthenticated emails. DMARC also defines another DNS record to store the sending domain’s public key.

Importance of Email Authentication for Email Security for Businesses
Email authentication is a critical aspect of ensuring email security for businesses. It serves as a means of verifying the sender’s identity, thus preventing malicious actors from disguising themselves as legitimate senders. Implementing email authentication protocols, such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, provides a multi-layered approach to authenticating the source of an email and protecting against spoofing and phishing attempts.
SPF enables email systems to authenticate that the domain from which a message is being sent is, in fact, a domain that has been authenticated as the owner and controller of said domain. DKIM digitally signs mail sent by servers, enabling domain authentication and validation that the message was legitimately sent from the specified domain.
DMARC builds upon the authentication provided by SPF and DKIM and enables domain owners to specify how receiving servers should handle unauthorized or unauthenticated messages. Thus, these are necessary for complete and efficient email authentication and security.
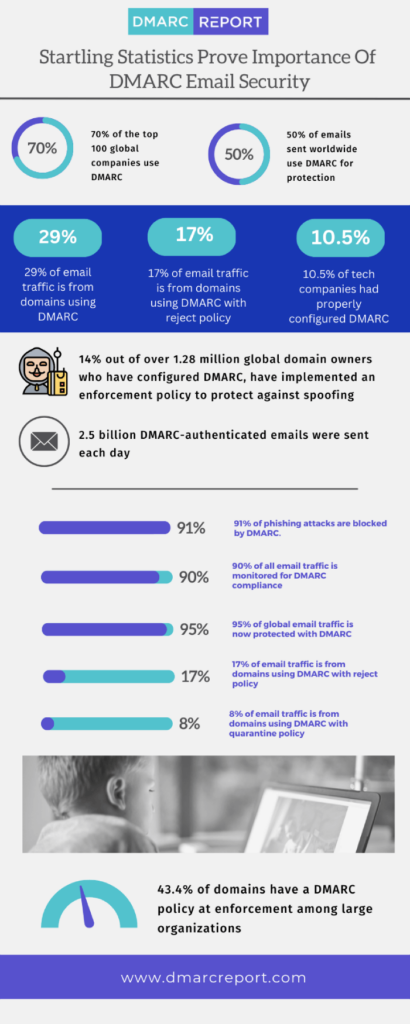
Utilizing these protocols can significantly enhance a business’ email security by providing a robust mechanism for detecting and blocking malicious emails, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage. Businesses must prioritize implementing and adhering to email authentication standards to safeguard against the ever-evolving threat landscape of cyber attacks.
Final Words
Emails have become a primary target for phishing attacks, posing a growing threat to individuals and organizations. As threat actors have started using more sophisticated tools such as phishing kits, staying vigilant and educated on spotting and avoiding these threats is imperative. Businesses must protect themselves and their customers from these increasing email threats, and leveraging SPF, DKIM, and DMARC should be at the top of their list!





