Mcdonald’s Application Tips, Ingram Micro Recovers,Gemini Email Exploit
Hey folks! It’s week 3, and we hope you have managed to survive the malicious intentions of threat actors around you. You see, only practicing cyber hygiene and having cyber awareness can help you in this era of sophisticated cyberattacks.
We are back again with our weekly dose of cyber updates. This time, we will discuss McDonald’s massive security incident, talk about Google Gemini’s ability to generate legitimate-looking malicious email summaries, and focus on how Ingram Micro is slowly getting back on track.
Let’s get started with the details that matter!

See this if you’re planning to apply at McDonald’s!
One of the most popular fast food joints across the globe, McDonald’s experienced a massive cyber mishap this June, when thousands of applicants used McHire to apply for work at McDonald’s. The cyber incident took place because of the flaws in McHire, the hiring platform used by McDonald’s.
Security experts Sam Curry and Ian Carroll have detected a couple of flaws in the platform. They tested the chatbot (Olivia) associated with McHire and found out that with the help of default credentials “123456” in passwords and usernames, one can easily access the admin interface of restaurant owners. Further, backed by IDOR or API, one can conveniently access any inbox to gain access to the personal data of 64 million applicants.

The leaked data includes highly sensitive information such as email addresses, residential addresses, names, phone numbers, candidacy statuses, and more.
The two security experts informed McDonald’s and Paradox.ai, the developer of the chatbot Olivia, about the flaw. Within two hours of reporting, McDonald’s changed the default credentials. As of now, there’s no evidence indicating that threat actors have attempted to access the data of 64 million applicants.
This blunder comes with a few critical cyber lessons:
1. Make sure you change your default credentials
Never use your default password. Change it to create a strong password that cannot be easily penetrated or cracked for malicious purposes.
2. Secure your LLM
LLMs should be equipped with limited capabilities to minimize the risk of compromise and subsequent rogue incidents.
Ingram Micro is finally getting back on track after the cyberattack!
Here’s the good news for Ingram Micro customers!
Their website is up and running once again.
Ingram Micra experienced a ransomware attack on July 4th, just before the holiday weekend began. They are working closely with team members and other authorities to cope with the cyber mishap. The IT distributor giant is right now trying its best to cater to the needs and expectations of its customers and other significant stakeholders.

Threat actors used ransomware to target Ingram Micro’s internal systems. As a result, the IT distributor took its systems offline for some time. They took mitigation steps to limit the extent of the ransomware attack. Also, Ingram Micro filed an 8-K form with the US Securities and Exchange Commission. It has also been working with third-party forensic experts and law enforcement agencies to investigate the cyberattack.
So far, there has been no clarity around the key perpetrator. However, a report by Bleeping Computer suggests that the SafePay ransomware gang is involved in this cyber mishap. SafePay is believed to have come out of LockBit.
Ingram Micro managed to contain the threat attack on Tuesday.

Google Gemini can be exploited to generate malicious email summaries!
Google Gemini comes with a flaw that can help phishing actors generate malicious email summaries. The email summaries may look genuine or legitimate, but they may come with warnings or malicious instructions that can redirect users to phishing sites.
This type of attack uses indirect prompt injections that are hidden in plain sight in the email content. Such prompt attacks have been reported multiple times since 2024. Despite various safety measures being deployed, threat actors have continued to exploit Gemini email summaries successfully.
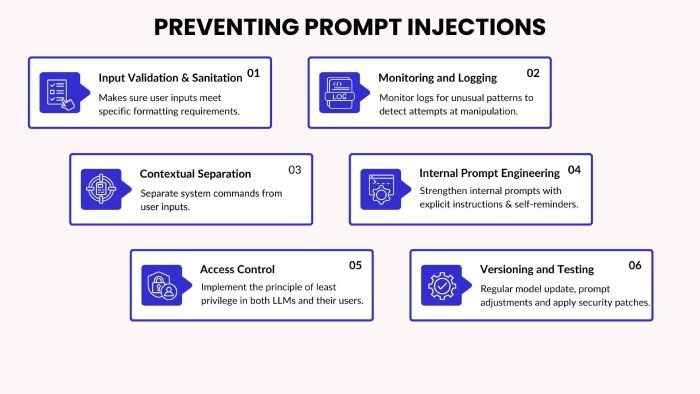
Mozilla’s bug bounty program recently disclosed a prompt injection attack on Gemini. Threat actors use an invisible directive for Gemini to come up with an email. The malicious instructions stay hidden in the text of the email in the form of HTML and CSS commands. Since there are no malicious links or attachments, these emails easily pass the authentication checks and safely land in the inbox of target users. When a user opens the email and asks Gemini to create a summary of the email content, Gemini will follow the instruction.
To safeguard against such cyber threats, organizations must implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols to strengthen email security and protect users from phishing and spoofing attacks.

Google’s spokesperson has stated that they are implementing the necessary mitigation steps to prevent prompt injection attacks in the future. They are also highly confident about their “robust defense” system.
Meanwhile, experts advise users to stay alert and take precautionary measures to avoid such cyber mishaps. They must not trust Gemini summaries blindly. Also, implementing a post-processing filter to scan Gemini output can be quite helpful.






