Top 8 email security protocols that can shield your brand’s reputation

We hate to break it to you, but no matter how much you try, you cannot be invincible against malicious cyberattacks. Cybercriminals realize that email is the backbone of your organization’s communication infrastructure, which is why they leave no chance to exploit vulnerabilities. From phishing attacks to domain spoofing and business email compromise (BEC), threat actors leverage ever-more complex tactics to break into systems, siphon sensitive data, and inflict monetary damage.
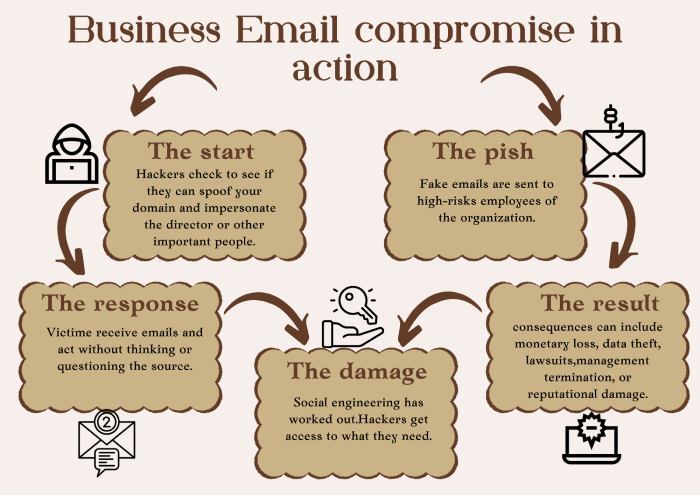
It only takes one fraudulent email to trigger sensitive data compromises, financial gain, and reputational harm that could last for years.
So, one thing is clear: email security is not a choice—it’s a necessity.
The good news is you don’t have to risk leaving your defenses to chance. Email security measures have come a long way since the days of basic spam filters and rudimentary firewalls. Modern security protocols concentrate on authenticating the sender, protecting the integrity of the message, and preventing unauthorized usage of your company’s domain. These protocols operate in the background to confirm the legitimacy of emails before they reach the inbox, thereby reducing the chances of phishing, spoofing, and other malicious activities going undetected.
Speaking of email security protocols, there are so many options out there, where should you start? To make things easier for you, we’ve rounded up the top eight email security protocols that should be part of every organization’s security strategy. Let us take a look at them.
What are the most important email security protocols?
Lately, email security has become the talk of the town, and rightly so, given the cyberthreat landscape of today. It has now become necessary for organizations to secure their email communications. To do so, it is important that you understand which security protocols to prioritize, especially when there are so many of them out there.
After all, it’s not just about implementing a protocol for the sake of it, it is about investing in your organization’s security and future.
The most important email security measures not only verify the authenticity of senders but also verify the integrity and legitimacy of your emails. With the implementation of these best measures, you are able to properly minimize the danger of email attacks while securing your communication.
Let’s get into the ones that must be at the top of your list.
1. SSL/TLS for HTTPS
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are security standards that protect your information as it moves from location to location, such as between your web browser, email app, and servers. SSL was initially a widely adopted standard, developed back in 1995, but it was a bit flawed.
SSL was the first widely used protocol, introduced back in 1995, but it had some weaknesses. To fix those, TLS came along in 1999 with stronger encryption, better ways to verify who is sending or receiving data, and stronger protection to keep information from being altered.
Notice the ‘S’ in HTTPS? That stands for ‘Secure,’ which means that the connection relies on SSL/TLS to establish an encrypted link. In the context of email security, SSL/TLS guarantees that messages are securely transmitted between servers without exposing sensitive information to interception.
2. SMTPS
Sending a message through mail is pretty uncomplicated until you realize that someone can open and read it along the way. That was how the original Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) worked when it first came into practice. There was no intention for security, so emails were essentially sitting ducks for hackers. This is where SMTPS enters the picture. It works like a locked, tamper-proof envelope for your emails as they move from one server to another. SMTPS employs TLS (Transport Layer Security) to encrypt your email into unreadable messages before sending them. So, even if someone tries to intercept them, they can’t read it. But here’s the catch—SMTPS only secures emails when being sent. The moment the email arrives in the recipient’s mailbox, it’s no longer protected by SMTPS.
3. StartTLS
StartTLS is not exactly an email protocol; it is an email protocol command that helps make connections secure by telling the server to upgrade an unencrypted connection to a secure one with the help of SSL or TLS. This means that emails can be sent safely without requiring a separate secure connection from the start.
When you send an email, your email client first connects with the server without encryption. A StartTLS command is then initiated, asking the server to shift to an encrypted connection. If the server supports encryption, it encrypts the communication and protects the email from being caught in transit.
4. SMTP MTA-STS
The next email security protocol that should definitely be a part of your security strategy is SMTP MTA-STS. It ensures that the emails that you send always go through an encrypted connection. To ensure that your emails are secure with SMTP MTA-STS, you must set an MTA-STS policy on your mail server. When you send an email, your mail server checks whether the recipient’s server enforces this policy. If it does, the email is sent securely. If not, the email will not be sent at all—because sending it over an insecure link could leave it vulnerable to hackers.
One of the good things about this protocol is that it prevents attackers from misleading servers into bypassing encryption—a common practice in certain types of cyberattacks. So, with this protocol in place, your emails are significantly more secure while they’re being transmitted between servers.
5. SPF
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is a security protocol that prevents attackers from sending spoofed emails from your domain. Without SPF, it is easy for someone to spoof your email address to make people open phishing emails or reveal sensitive information. That is why having SPF implemented is so crucial—it prevents only legitimate emails sent on your behalf from reaching the recipient’s inbox. This brings down the chances of your emails being filtered out or marked as spam.
That being said, even though SPF is an important aspect of your defense mechanism, it does not suffice by itself. It must be used alongside other authentication protocols, such as DKIM and DMARC, for a stronger defense.
6. DKIM
Speaking of strengthening your email security, DKIM or DomainKeys Identified Mail is another protocol that works in tandem with SPF to secure your outbound emails. This protocol ensures that the emails that you send are authentic and haven’t been altered in transit. It does this by attaching a digital signature to emails sent from your domain. When the recipient’s mail server receives the email, it verifies that signature to ensure the email actually originated from you and wasn’t altered.
DKIM makes it harder for attackers to alter your emails or spoof email senders on your domain. If the signature is verified, the email is considered trustworthy and let in. If not, the email can be rejected or marked as suspicious.
7. DMARC
The third and perhaps the most important authentication protocol in the trio (SPF, DKIM, and DMARC) is Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance. First, we have SPF that verifies whether an email is coming from a permissioned server, then DKIM ensures the email wasn’t altered during transit, and DMARC goes one step ahead and ties it all together.
It tells receiving servers how to handle emails that fail these tests—whether to deliver, quarantine, or reject them. This allows you to dictate how your domain is handled when someone tries to misuse it. Without DMARC, even with SPF and DKIM, spammers can still get through.
What makes DMARC stand out from them all is its reporting feature. It sends you regular reports telling you who is sending emails on behalf of your domain, both authorized and suspicious. With these reports, you are able to spot any unauthorized action before it could lead to something detrimental.
8. Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are another way to prevent scammers from misusing your domain. When you send an email, it’s encrypted with a private key. They defend your organization against phishing and other email attacks by authenticating the sender’s identity and ensuring the message is legitimate.
This is how these certificates work: the recipient uses a public key associated with your certificate to decrypt and view the message. This only allows the intended receiver to see the email and verifies that nobody has interfered with it during transit. Including digital certificates puts an additional security layer on your emails, safeguarding your communications and making them reliable.
Let’s face it: there are too many options out there to secure your emails, but you cannot randomly pick and choose. After all, email security is not just about applying any given protocol—it’s about using the correct combination that plays off each other to give you all-round protection.
If you are struggling to get started with your email security journey, you’re in the right place! Our team of experts is here to help you with the primary email authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, and DMARC) and ensure that you’re always a step ahead of the attackers in your defense strategy.






