Receiving the Maximum Benefits From DMARC Reporting and Monitoring
DMARC reporting and monitoring is the practice of choosing to receive DMARC aggregate and forensic reports. These are detailed reports that include insights on email activities that businesses study to learn about false positives and domain exploitation instances.
If evaluated adequately and regularly, you can prevent potential financial and reputational damages caused by phishing attacks attempted in your name. The Cyber Security Breaches Survey 2022 showed that 83% of organizations that suffered a cyber attack in the past year said that it was caused by phishing. Let’s understand how businesses can prevent such unfortunate events by leveraging the best features of DMARC reports.
Benefits of DMARC Reporting and Monitoring for Businesses
You receive DMARC reports in an XML format, which is difficult to decipher by people lacking proficiency in coding. You can use a converter that translates such reports into simple English language that can be understood by anyone. You can choose to convert the data in a simple tabular form or other convenient formats. Learn how to go through a DMARC report here.
Now that you know that you can easily decipher aggregate and forensic reports, let’s understand why businesses should even care to start receiving them in the first place.
Early Threat Detection and Prevention
You come across potential vulnerabilities and security loopholes that can cause significant operational, financial, and reputational damage. The identification of anomalies, patterns, and trends prepares you to stay vigilant, put in preventive measures, and come up with mitigation strategies.
Improved Visibility and Control Over Email Infrastructure
DMARC reports show you how your domain is being treated at the recipients’ ends so that you can take care of the malicious and unwanted email traffic originating from your domain.
Enhanced Email Deliverability Rate
Email deliverability is the ability of emails to land in the inboxes. Understanding the authentication status of your emails allows you to take corrective actions to improve email deliverability. By configuring DMARC policies, you can specify how receiving mail servers should handle unauthenticated emails, helping to reduce the likelihood of legitimate emails being marked as spam.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Some industries and regulations may require organizations to implement email authentication measures. By using DMARC and regularly evaluating reports, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to email security and compliance with industry standards.
Continuous Improvement
Regularly reviewing DMARC reports allows organizations to fine-tune their email authentication policies. This iterative process helps improve the effectiveness of the email authentication mechanism over time, which permits adaptation to changes in the email landscape and emerging threats.
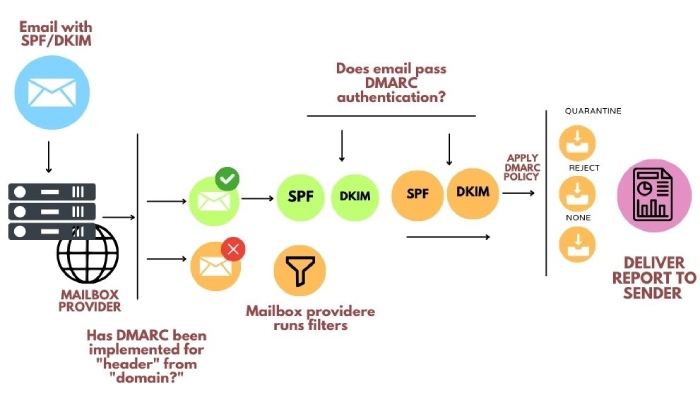
DMARC Reporting Steps
A standard DMARC reporting process flows in the following steps-
Access
Accessing DMARC reports begins with publishing a DMARC record in the corresponding Domain Name System or DNS. The DMARC record instructs recipients’ servers on how they should deal with email messages that fail DMARC authentication checks. While generating a DMARC record, you are required to add email addresses where you want to receive aggregate and forensic reports for monitoring and analysis.
Differentiate
Two types of DMARC reports are generated:
Aggregate or RUA Reports
Recipients’ ISPs and service providers generate DMARC aggregate reports based on the policy published in the domain’s DMARC record. A standard RUA report includes statistical insights on the volume of emails received along with their authentication results.

Domain owners receive these reports periodically and can choose the frequency, usually ranging from daily to less frequent intervals like fortnightly or monthly.
Ideally, a domain owner or a person in charge of email authentication parses the information to gain insights into the health of the email communication system. They identify sources of legitimate emails, detect unauthorized senders, and assess the overall effectiveness of their DMARC policy.
Forensic or RUF Reports
Forensic or RUF reports are more detailed than aggregate reports, as they provide specific details on individual email messages that fail DMARC authentication checks. This includes the full headers and content of the problematic emails, allowing domain owners to conduct a thorough analysis of the failed authentication incidents.
Similar to aggregate reports, domain owners specify one or more URIs where forensic reports should be sent. These URIs can be email addresses or web endpoints. DMARC Forensic reports are typically sent in real-time or near-real-time when an email fails DMARC authentication.
Some organizations integrate forensic report data with their security information and event management (SIEM) systems or other security tools for more comprehensive threat analysis and response.
Analyze
The analysis of DMARC reports includes focusing on the alignment and specified policy. Proper alignment means that the SPF protocol works adequately, which subsequently means that the return path or the SMTP ‘From’ address is the same as the ‘From’ header of the email.
You can choose either of the three policies;
- p=none: No action should be taken against messages that fail DMARC authentication.
- p=quarantine: Messages that fail DMARC authentication should be marked as spam.
- p=reject: Messages that fail DMARC authentication should be bounced back.
What Does DMARCReport Offer?
We at DMARCReport parse information by analyzing the following:
Authentication Results
We start by looking at messages that fail SPF and DKIM checks as they point towards potential phishing attempts, email interception, message forwarding, and configuration issues.
Headers and Metadata
Parsing of email headers to identify senders’ IP addresses, transit routes, and modifications made after dispatching from original sources.
Attachments and URLs
Next, we take a close look at attachments and links to highlight suspicious or malicious content smartly embedded in the email.
Sources
Lastly, our DMARC report and monitoring mechanism focuses on evaluating which IP addresses or servers are sending fraudulent emails on behalf of your brand.
In summary, forensic and aggregate DMARC reports provide granular details about email messages that fail DMARC authentication. These are crucial tools for incident response, forensics, and maintaining the security of email communication by allowing organizations to quickly identify and address potential threats.
So, get in touch with our experts to understand how we can help you stay abreast of email-based cyber menaces that could impact your business reputation, operation, and finances.







