What is a DMARC Policy, and How Does It Affect Sending My Emails?
Listen to this blog post below
This text will delve into the details of DMARC and share how it influences the sending of emails. Read on to how this email authentication protocol works.
Email is the primary communication tool for businesses and individuals alike. However, the threats surrounding emails, such as phishing and spoofing, are ever-increasing, begging for robust email security measures to protect email senders and receivers.
Luckily, DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) can keep these threats at bay and do wonders for your email if appropriately used. Let us see how.
What is DMARC?
DMARC is an email authentication protocol that allows senders to protect their domain from unauthorized use and prevents malicious actors from impersonating their identity. It enables domain owners to specify policies for how email receivers should handle their emails, enhancing email security and reducing the risk of domain abuse.
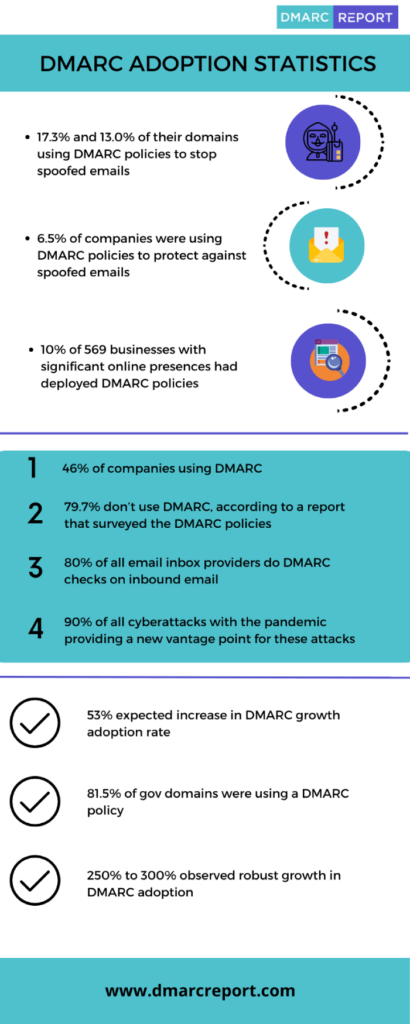
What are the Components of DMARC?
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): SPF allows domain owners to publish a list of authorized sending servers for their domain. When you receive an email, the server verifies if the sending server’s IP address matches the allowed list. If not, the email may be flagged as suspicious or rejected.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): DKIM utilizes public-key cryptography to sign outgoing emails with a digital signature. The recipient’s email server can validate the signature using the corresponding public key published in the sender’s DNS records. If the signature is valid, it ensures that the email originated from the claimed domain and hasn’t been tampered with.
- DMARC Policy: DMARC policies instruct email receivers on handling emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks. There are three primary policy options: “none,” “quarantine,” and “reject.” The “none” policy allows the recipient’s server to collect DMARC reports without taking immediate action. The “quarantine” policy suggests placing suspicious emails in the spam or quarantine folder, while the “reject” policy instructs the server to reject such emails outright.
How Does it Affect the Sending of Emails?
DMARC can be a tool in the arsenal of organizations. Here is what it does for your emails:
1. Improve Email Deliverability
Looking to improve your email deliverability? By authenticating emails using SPF and DKIM, DMARC helps email providers and ISPs (Internet Service Providers) distinguish between legitimate and malicious emails. When your emails pass the DMARC checks, they are more likely to be delivered to the recipient’s inbox, ensuring better visibility and higher chances of engagement.

2. Reduced Risk of Email Spoofing and Phishing
By configuring DMARC policies to reject or quarantine emails that fail authentication, you can easily protect your domain from unauthorized use and prevent threat actors from impersonating your brand. DMARC also helps safeguard your recipients from falling victim to phishing attacks, and preserve your brand reputation.
3. Enhanced Brand Integrity and Trust
Implementing DMARC demonstrates your commitment to email security and establishes trust with your recipients. When your emails consistently pass DMARC checks, recipients can be confident that the messages they receive are genuinely from your organization.
4. Better Inbox Placement
Email providers and ISPs increasingly rely on DMARC policies to determine the fate of incoming emails. When your DMARC policies are correctly configured, your emails have a higher chance of landing in the recipient’s primary inbox instead of being sent to spam folders.
5. Ensure Compliance
Many industries, especially those dealing with sensitive information like Finance and Healthcare, have regulations regarding email security. Implementing DMARC can ensure compliance with these regulations, demonstrating your commitment to protecting customer data and maintaining the integrity of your communication channels.
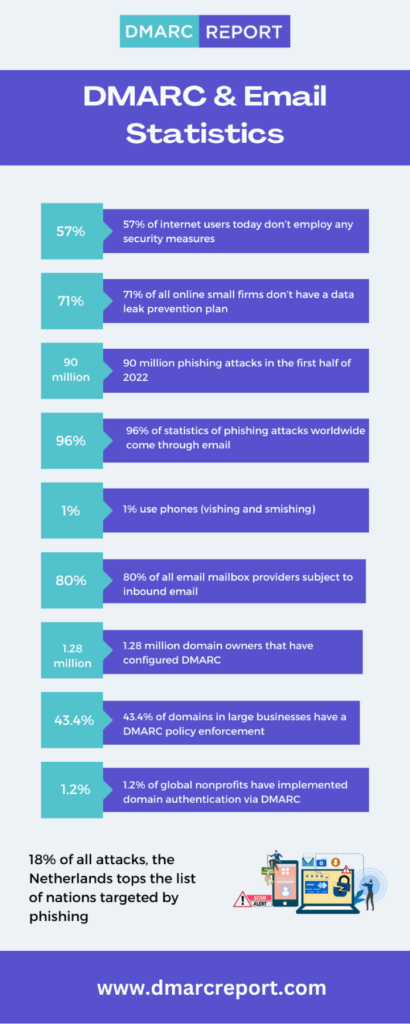
What are the Best Practices for DMARC Implementation?
Here are the best practices for organizations to follow when implementing DMARC:
- Implement Gradually: Implementing DMARC can be a complex process, particularly for organizations with a large email ecosystem. You should start with a “none” policy to collect DMARC reports and gradually transition to other policies after analyzing the reports.
- Monitoring and Analysis: Regular DMARC monitoring and analysis of DMARC reports are crucial for understanding email authentication failures, identifying legitimate senders, and spotting unauthorized activity. You can make informed decisions and fine-tune your DMARC policies to achieve optimal results if you continually monitor DMARC.
- DMARC Analyzer and Monitoring DMARC: To fully leverage the benefits of DMARC, organizations can utilize DMARC analyzer tools. These tools provide insights into email authentication results, offering detailed reports and analytics.
- Collaboration with Email Service Providers: Collaborating with ESPs (Email Service Providers) is a must when implementing DMARC. ESPs can assist with DMARC implementation, guide best practices, and help resolve any technical challenges that may arise during the process.
Final Words
In an era where email-based threats pose significant risks, DMARC emerges as a powerful tool to combat domain abuse, protect brand reputation, and enhance email security. By leveraging SPF, DKIM, and DMARC policies, organizations can establish trust, ensure email deliverability, and fortify their email infrastructure against malicious attacks.
Implementing DMARC requires careful planning, continuous monitoring, and collaboration with ESPs, but its security and brand protection benefits make it an indispensable component of modern email communication.







