Secure Your Email Communication By Achieving The Highest Authentication Standards With DKIM Signatures

While emails have made networking more manageable, they have also become a channel for nefarious agents to employ spoof messages to impersonate brands and businesses. This issue has been a significant concern for over a decade since many phishing attacks occur through email spoofing.
Even though the security of emails has been a constant topic of heated discussions, no complete solutions have ever surfaced. However, with the DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), emails have become far more secure than earlier. The heart of the DKIM signature system is a unique public-private key pair.
What is DKIM Signature?
This section has more information on what a DKIM signature is and how email communication can benefit from using it. A DKIM signature is an encrypted digital key that helps service providers authenticate an email. Such a protocol stems from the notorious possibility of impersonating user identities by malicious actors to steal sensitive data or corrupt an information system network.
The standard protocol used to send emails over a network is SMTP. But it doesn’t involve any authentication measures to verify the sender. Authentication protocols work by connecting details found in an email’s header with the information recorded on the domain name server (DNS) of a user’s domain. The DKIM signature is one such protocol formed by an amalgamation of a Yahoo development program, ‘DomainKeys’ with Cisco’s ‘Identified Internet Mail.’ DomainKeys verifies the DNS domain of the email sender, while Identified Internet Mail is the digital signature segment.
How Does The DKIM Signature Work?
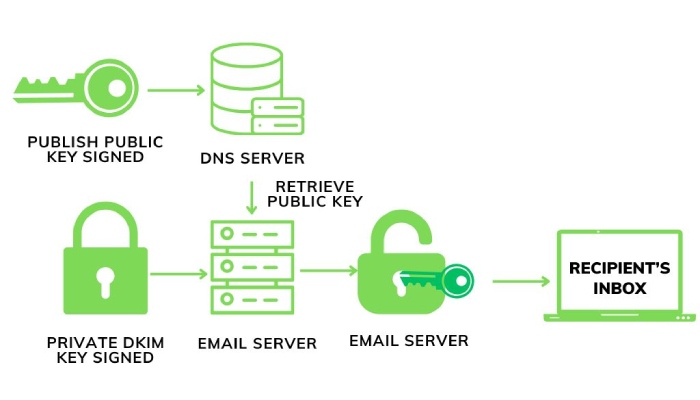
DKIM authentication involves a DKIM record published in the DNS (Domain Name System). It contains information constituting a pair of keys known as the public and private keys. This pair comprises the encrypted digital signature unique to the user and can be verified using the DNS record. In the DKIM authentication system, the private key is also included in the email’s header in its encrypted form. DKIM allows users to compare the header information of an email with the relevant domain, and the information registered on the DNS confirms the email’s authenticity.
Mail transfer agents (MTAs) can use the DKIM signature to understand where to extrapolate the information on the public key to verify the user’s identity. If the information on both keys matches, the email is more likely to get delivered to the inbox. And if there is no match between the keys or the DKIM signature is not found, that email is most likely to get rejected or land in the spam folder. DKIM aids mail servers in resolving how to best filter the incoming emails.
Verifying Your DKIM Signature
At times, the DNS records and DKIM signatures can get intricate. However, various online tools can help check whether the authentication protocols are perfect. Apart from these tools, users can also verify their DKIM signatures by other methods, such as sending a test email message to a Gmail account. After sending the message, they can open the email and click on the arrow next to the reply option. Once clicked, the user can select ‘Show original,’ and if it displays the signature of their domain name, their DKIM signature is sound.
Comparing DKIM With SPF
Sender Policy Framework or SPF is another authentication protocol like DKIM which authenticates users and aids in preventing spoofing attacks. Unlike DKIM, which uses digital keys to verify a sender, SPF maintains a record consisting of a list of domains or servers, including your email service provider, authorized to send emails on behalf of a specific domain.
One drawback of SPF is that it breaks down during email forwarding, while DKIM signature does not. However, a DKIM signature can get faked, making it necessary to rotate the keys regularly. This comparison lets anyone understand that for having a stronger email authentication, a combination of DKIM signature along with SPF is a better choice.
Final Words
The ability to communicate with people through email is one of the most significant advantages of digitalization. However, malicious agents take undue benefit from the relationship between organizations and individuals.
Nevertheless, the unique method of email authentication using DKIM signatures helps verify senders’ information and ensure that only verified emails reach the inbox. DKIM is a valuable tool, and many major email service providers, including Google, Apple Mail, and Outlook, look for DKIM signatures for email authentication today.






