The Importance of DMARC For Email Marketing and How to Get Started With it
Email marketing is the backbone of the new-age online business era, where newsletters and other forms of marketing content are dispatched in bulk with the intention of attracting prospects into opening them and clicking on the links. Upon clicking the links, the recipients are taken to the products or services pages, hoping they will make a purchase and increase sales.
All this sounds like a nice profit-making strategy, but what about the case when these emails don’t show up in the inboxes of the target recipients? We are talking about situations when emails land in the spam folder or bounce back.
This happens due to a low email deliverability level and poor domain reputation. That’s why DMARC for email marketing is a solution that marketing teams have adopted for quite some time now.
DMARC for email marketing is the concept where messages sent from unauthorized sending sources are marked as spam or rejected so that only genuine messages pass the filter. This prevents phishing and spoofing attacks in addition to improving email deliverability and sender reputation significantly.
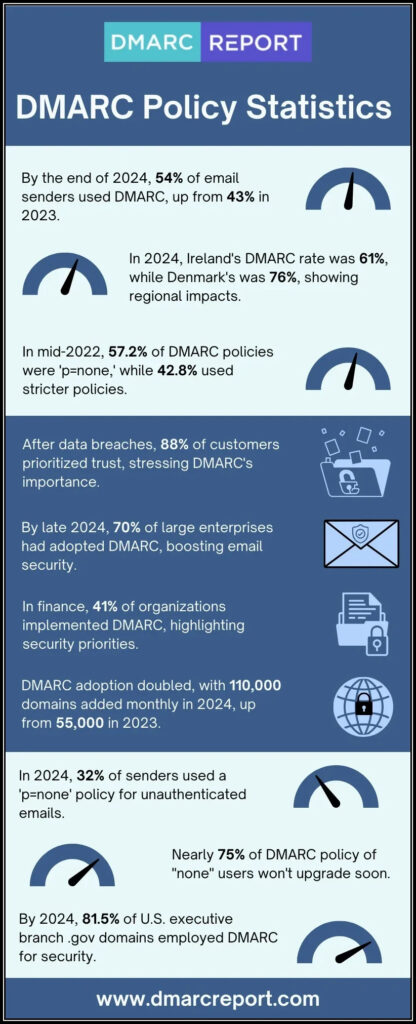
We have curated this blog that explains why email marketers should care to deploy SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for their platform. In the end, we have also explained the DMARC setup.

What is DMARC and How Does it Work?
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance. The DMARC authentication process includes a DMARC TXT record that instructs recipients’ mail servers how to deal with illegitimate emails sent from your domain name.
To understand how DMARC works, you need to be familiar with SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), which are the basic email authentication protocols. So, SPF works on the principle of allowlisting (or whitelisting), where a domain administrator has to create and submit a list of IP addresses and email servers that they allow to send emails using their domain. Any sending source outside of the list is considered unauthorized, and any message sent using it gets rejected or gets placed in the spam folder.
DKIM, on the other hand, uses cryptographic keys to verify the sender’s authenticity and confirms that no changes were made to the email content in transit.
DMARC verifies the genuineness of email senders on the basis of SPF and DKIM results, which means an email message has to pass at least one of these protocols in order to pass DMARC authentication checks and protect companies or businesses from becoming victims.
For email marketers, it’s an email authentication add-on designed to align with any pre-existing inbound email authentication process.
Emails failing DMARC authentication checks are subjected to one of these actions, also called DMARC policy, and domain owners choose which policy they want to implement.
- The None Policy (p=none): This states that no action has to be taken against emails failing the DMARC check.
- The Quarantine Policy (p=quarantine): This states that illegitimate and suspicious email messages have to be marked as spam.
- The Reject Policy (p=reject): As per this DMARC policy, illegitimate and potentially fraudulent emails have to be rejected, which means they bounce back to the sender.
Benefits of DMARC for Email Marketing

While DMARC might not directly impact the content or design of your email campaigns’ strategies, however, it brings in a bunch of benefits for the marketing team-
Protection from Phishing and Spoofing
DMARC DNS records protect company domains and customers from getting tricked into sharing sensitive and confidential details. Emails sent from spammers get flagged and don’t show in the inboxes of recipients, saving them from opening and engaging with them.
Good Brand Reputation
DMARC safeguards the reputation of a company by disallowing exploitations of domains and malicious activities attempted in its name. It ensures that recipients can trust that emails claiming to be from your organization are legitimate. Moreover, it doesn’t give your competitors a chance to win over you by taking advantage of a spoiled brand image.
Satisfied Customers and Prospects
Email security and data protection build trust with your customers, giving them the confidence to open and engage with your marketing emails as they trust your organization. This fosters relationship with them and increases sales.
Visibility and Reporting
DMARC provides reporting mechanisms that allow senders to receive feedback (in the form of rua and ruf reports) on the handling of their emails by email receivers. The reports help organizations get information into their email ecosystem, identify unauthorized use of their domains, and take corrective actions.
DMARC reports allow domain owners to adjust the percentage of emails that are subjected to DMARC policies, which minimizes the instances of false positives for genuine emails sent on behalf of the business.
Regulatory Compliance
In some industries and regions, compliance with email authentication standards, including DMARC, is becoming a requirement. Implementing DMARC can help organizations meet regulatory standards related to email security and privacy. Non-compliance to the DMARC protocol can make you liable to lawsuits and other problems.
Learning to Set Up DMARC
Malicious people are always on the hunt to exploit vulnerable resources, including the email domain of a reputed organization. So, let’s learn how to address such problems through DMARC deployment.
Assess and Define
Since DMARC functions on the basis of SPF and DKIM results, you first need to create SPF record and DKIM records and update them on DNS (Domain Name System). Then, you need to determine which of the DMARC policies you should implement in your DMARC DNS record– none, quarantine, or reject.
Generate a DMARC Record
Use one of the online tools to produce a DMARC record that includes your desired policy, and it’s highly recommended to choose to receive rua (aggregate) and ruf (forensic) reports for monitoring.
You can also receive reports in the inbox of an email address/ account outside of the domain. This is done using the external domain verification process.
Here’s an example of a DMARC record-
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:reports@example.com; ruf=mailto:forensic@example.com
Let’s see what each element means-
- The v tag specifies the SPF version.
- p=none means the policy chosen is ‘none,’ which instructs the mail server of a receiver to take no action against illegitimate messages.
- rua=mailto:reports@example.com specifies the email address where DMARC aggregate reports should be delivered.
Publish the DMARC Record
Save the TXT DMARC record created earlier and publish it in your DNS setting.
Evaluate DMARC Reports
Now, your domain is protected against email spoofing and phishing scams, in addition to having a good email delivery rate and domain reputation.
Start monitoring forensic and aggregate reports once you start receiving them. These reports are originally in XML format, but we can help you decipher them in simple English.







